Varicose veins are a disease that is accompanied by a thinning of the venous wall, an increase in the diameter of the lumen of the veins and the formation of nodular dilations similar to aneurysms. Any vein can be involved, but it is most commonly diagnosed in the lower extremities. Treatment of varicose veins includes drug therapy and surgical methods. Lack of therapy increases the risk of dangerous complications.
Causes of varicose veins
The underlying cause of the disease is not fully understood. We can only name provoking factors that increase the risk of developing pathology:
- genetic predisposition. If one of the parents had a disease, then it can develop in children.
- long static loads. Working while standing causes stagnation of blood in the veins, which leads to their expansion and provokes the development of varicose veins.
- Lack of movement.
- Excessive loads, including professional sports.
- Excess weight, which leads to increased pressure in the vessels of the lower extremities.
- Pregnancy, in which the pressure in the vessels of the small pelvis and lower extremities increases, and the elasticity of the vascular wall also changes.
- Wearing shoes with high heels, which disrupts the contractility of the calf muscle involved in the movement of blood through the veins (the so-called "muscle pump").
- Inadequate nutrition (in particular, lack of fiber) leading to constipation, which causes increased pressure in the vessels of the small pelvis and lower extremities.
- Bad habits.
- Hormonal imbalances.
These are common causes of dilated veins. If in women the first signs of venous insufficiency appear during pregnancy or immediately after childbirth, in men, as a rule, the disease makes itself felt after 40 years. The leg vessels are most frequently involved. The treatment of varicose veins of the lower extremities in both sexes is practically the same.
Symptoms of varicose veins of the lower extremities.
Officially, the disease is divided into three stages:
- Compensation.
- Subcompensation.
- Decompensation.
In addition, there is an international classification that distinguishes classes:
- C0. There are no signs of vascular damage, but the patient complains of varicose veins.
- C1. Expansion of small superficial veins is noted.
- C2. Dilated veins are revealed during visual examination.
- C3. The patient complains of swelling of the tissues, pain, excessive fatigue after a day's work.
- C4. The first symptoms of trophic disorders are determined visually.
- C5. Trophic changes appear, but ulcers heal. There may be scars.
- C6. Trophic changes are pronounced, there are active ulcers.
The degree of pathology is determined on the basis of the results of a visual examination, instrumental diagnostic methods and existing signs of a chronic disease.
The first symptoms can be called:
- Increased leg fatigue.
- Swelling of the tissues, especially pronounced in the evening, which passes after a short rest.
- Pain sensations.
- Characteristic heaviness in the legs.
- Nocturnal cramps in calf muscles.
- Burning sensation along the course of the vein.
The pain is especially significant. It never radiates to the thigh or heel, but is always noticeable at the location of the affected vein and is painful in nature. Often the sensations are exhausting and prevent sleep. After sleeping, the pain subsides.
At the initial stage, there are no signs of damage to the saphenous vein, but changes are already taking place. The process can take several years, so the treatment of varicose veins often begins when there is already a pathology class 3-4. Over time, the clinic increases and the severity of the symptoms of venous insufficiency increases:
- Increased inflammation of the tissues. It is located mainly in the calf muscles. Like the pain, the swelling appears in the afternoon and goes away after a night's rest. It is important to distinguish edema in the calf muscles from swelling of the foot tissues. The latter indicates violations of the outflow of lymph.
- Itchy skin. It is noted along the vessels.
- Visual changes in the skin in the form of tortuous veins, presence of extensions.
- Skin changes as a result of circulatory disorders. There is cyanosis, thickening of the tissues, darkening is possible.
In the absence of therapy, the clinic is complemented by signs of tissue malnutrition, the appearance of trophic ulcers, eczema, etc. Violation of the venous valves can cause the following complications:
- thrombophlebitis. It is characterized by the formation of blood clots. Without help, the condition is life-threatening.
- venous thrombosisIt occurs with blockage of the vessel. It is manifested by severe pain, aggravated during physical activity.
- Pulmonary embolism. It occurs as a result of the separation of a blood clot. Due to its small size, it is possible to develop pneumonia or chronic heart failure.
- Trophic ulcers. The first signs are thickening of the tissues over the affected vein. Also, the tissues become thinner, an ulcer appears. The focus does not heal for a long time and does not respond to therapy.
Diagnosis of the disease
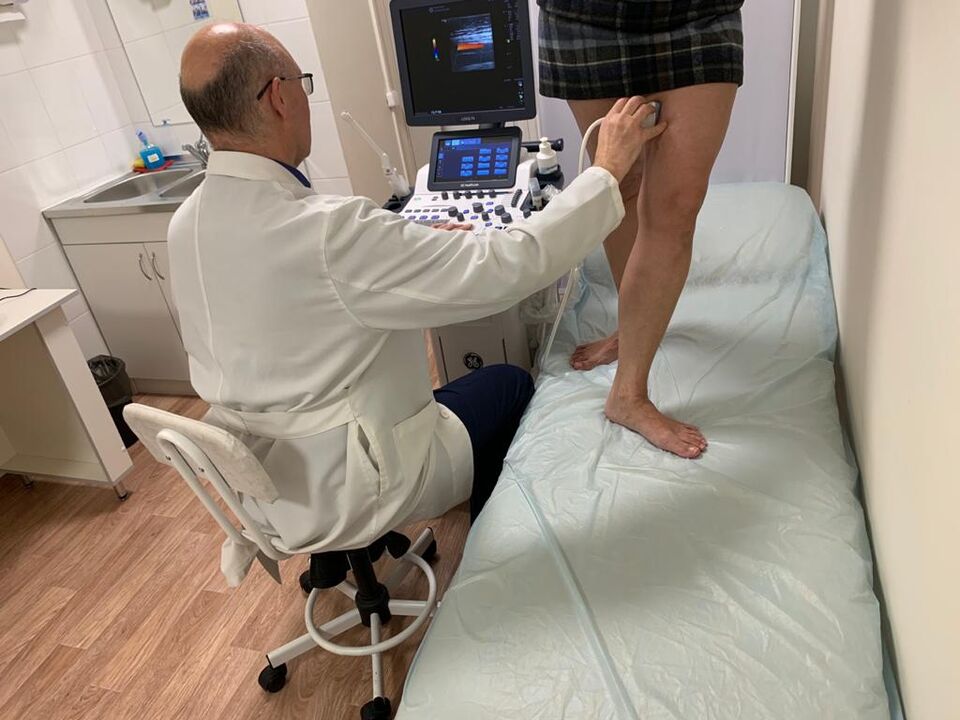
Despite the characteristic symptoms, it is impossible to make a diagnosis and start taking medication based only on the results of a visual examination.
Dopplerography is mandatory. This is one of the easiest ways to assess the vascular bed. It is based on determining the degree of change in the frequency of the sound signal reflected by the blood cells.
When performing ultrasound, angioscanning is performed, which makes it possible to assess the state of the vessel wall, as well as the direction of blood flow. The result will be a two-dimensional image of the veins with a reflection of the valves, possible blood clots.
In the event that the listed methods do not give a comprehensive answer, CT is prescribed. If thrombosis, angiodysplasia, and damage to the small pelvic veins are suspected, radiopaque phlebography is prescribed.
Treatment of varicose veins in the legs
A phlebologist is engaged in the diagnosis and treatment of pathology. It is this specialist whom you should contact at the first signs of diseases. In advanced cases, when conservative therapy does not give the desired effect, radical methods are used. In this case, the vascular surgeon is engaged in the removal of varicose veins.
Treatment methods are determined based on the results of the examination. In the initial stages, it is possible to use general and local drugs. When medications do not work, surgery is prescribed.
Conservative treatment
The main drugs are venotonics (phlebotonics). Available in the form of tablets and capsules, which have a systemic effect. Thanks to them, it is possible to normalize blood circulation and improve the state of the whole organism. In addition to tablets, you can use local remedies with a similar effect. These are creams and gels. They have a pronounced effect, but the effect lasts for a short time.
The action of phlebotonics is based on improving the elasticity of the blood vessels, reducing the permeability of the wall and eliminating congestion. Patients have a decrease in edema and normalization of hematopoiesis.
The use of antiplatelet and anticoagulant agents is allowed. They are indicated at a high risk of blood clots, as well as in their presence. Thanks to them, it is possible to destroy blood clots and reduce viscosity. Funds are used for a pronounced violation of blood viscosity, but with the risk of bleeding, their use is not allowed.
In addition to preparations, specialists prescribe compression stockings. It can be elastic bandages, socks, tights, stockings. The positive effect of its use is explained below:
- Bedding puts pressure on affected varicose veins and deep vessels.
- In the lower part of the legs, the vessels experience the most pronounced pressure from knitwear, which eliminates congestion.
- The vessels are constantly in a compressed state, so the operation of the valves becomes more efficient.
- By wearing underwear, the severity of edema and pain decreases.
Methods of surgical treatment of varicose veins.
In the absence of the effect of drug therapy, an operation is prescribed. Indications for its implementation are the following conditions:
- Failure of conservative treatment
- The first signs of thrombophlebitis.
- Pronounced expansion of the vascular wall.
- Significant inflammation of the tissues.
Effective treatment of varicose veins is possible using the following methods:
- Radiofrequency obliteration, which allows you to restore the structure of blood vessels.
- Laser coagulation, during which the affected areas are affected by a laser.
- Varadi technique with complete removal of the affected vessel.
- The Venaseal technique, thanks to which the valves of the veins are joined.
- Sclerotherapy, which allows you to "glue" the vessels from the inside.
Modern methods of treatment of varicose veins allow you to perform all the necessary procedures without hospitalization and let the patient go home. The choice of technique is determined by the doctor based on the results of the examination.
Prevention of pathology
Varicose veins are difficult to treat, and even after surgery, preventative measures must be taken to prevent recurrence. Some patients use drug therapy their entire lives and wear compression stockings. Pathology can be prevented as follows:
- Refusal to drag things.
- Wear shoes with a medium heel.
- Complete nutrition.
- Weight control.
- Normalization of the drinking regimen.
- Active recreation, swimming, cycling.
- Rejection of bad habits.
Compliance with preventive measures and attentive attitude to the body will help prevent the disease and notice deviations in time. Timely treatment of varicose veins eliminates the progression of pathology and the formation of complications.